 Do you have heel pain? If so, you’re not alone. In fact, the majority of Americans say that they have experienced foot and ankle pain at some point in their life. Moreover, of that majority, over 2 million suffer from heel pain due to plantar fasciitis. Fortunately, there is a nonsurgical option to treat plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is a highly advanced, non-invasive treatment that can alleviate pain due to plantar fasciitis. Keep reading to learn more.
Do you have heel pain? If so, you’re not alone. In fact, the majority of Americans say that they have experienced foot and ankle pain at some point in their life. Moreover, of that majority, over 2 million suffer from heel pain due to plantar fasciitis. Fortunately, there is a nonsurgical option to treat plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT) is a highly advanced, non-invasive treatment that can alleviate pain due to plantar fasciitis. Keep reading to learn more.
What is plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is inflammation of the plantar fascia, the band of tissue that goes along the bottom of your foot. This tissue connects your heel to your toes. When the plantar fascia inflames, it can cause heel pain. Usually, this pain is worse with activity and better with rest.
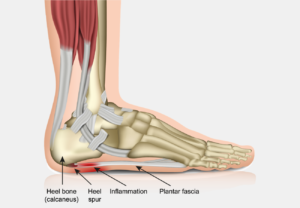 Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain in adults. Though it can affect anyone, it tends to affect runners and those who stand at work on hard surfaces more. Some patients may show a bone spur on x-rays, though the spur does not usually cause pain.
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain in adults. Though it can affect anyone, it tends to affect runners and those who stand at work on hard surfaces more. Some patients may show a bone spur on x-rays, though the spur does not usually cause pain.
Plantar Fasciitis pain includes:
- Pain directly under the heel
- Heel pain with activity
- Heel pain in the morning
- Pain in the heel when standing
In almost 95% of cases, plantar fasciitis can be treated without surgery. Conservative treatment is the first line of defense. These treatments can include stretches, anti-inflammatory medicine, ice, and arch support. Taping, casting, and physical therapy may also be used if necessary. For those who do not respond to these treatments, there is a noninvasive, nonsurgical option: Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT).
What is EPAT?
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology, or EPAT, is a nonsurgical, evidence-based treatment option for plantar fasciitis. This treatment was first developed in Europe and is now used worldwide to treat chronic inflammation. This highly advanced, FDA-cleared treatment works using shockwave therapy. Shockwave involves the use of acoustic pressure waves (or sound waves) to stimulate healing.
EPAT works by breaking up scar tissue and increasing blood flow in the affected area. That is to say, the acoustic pressure waves induce small microtraumas, tiny injuries to the tissue. The small microtraumas help regenerate the damaged tissue. This, in turn, enhances the body’s natural healing process. While EPAT has many uses, it is particularly effective for the treatment of plantar fasciitis.
EPAT can treat:
- Achilles pain
- Foot pain
- Heel pain
- Neuromas
- Plantar fasciitis
- Tendon pain
- Tendinitis, including Achilles tendinitis
What should I expect during EPAT treatments?
EPAT requires multiple treatments. Usually, patients have 3-5 treatments over 3-5 weeks. Yet, the number of treatments will also depend upon the patient’s condition or injury. Each treatment lasts about 10 minutes. Patients typically describe the sensation as pulsing but not painful. The treatment is in a doctor’s office and does not require any anesthesia. A typical treatment session will include:
- Healthcare provider locates the source of pain.
- Then, ultrasound jelly is applied to help conduct the sound waves.
- The healthcare provider then applies the applicator and gradually increases pulses.
- Once treatment is complete, patients may bear weight immediately and return to normal activities within 24-48 hours.
Pain relief can be immediate for some. However, on average it takes about 3-4 weeks to feel significant pain reduction, with maximum relief taking several months. This is due to the regenerative nature of the treatment, as the body heals itself.
What are the benefits of EPAT?
EPAT is a non-invasive treatment option. This means there is no surgery, recovery, or associated surgical risks. Also, EPAT has no known side effects or risks. In other words, EPAT is just as successful as surgery for plantar fasciitis, but without any unnecessary risks. This is great for patients who do not or cannot have surgery. While EPAT may not be right for everyone, it’s proven successful in over 80% of cases. Patients who had no pain relief with other treatments benefit most from this EPAT. Beyond pain relief, EPAT has many benefits, including:
- Improve the quality of life
- Increased mobility
- Treat the source of pain
- Regenerative treatment
- Enhance healing
- Improve circulation
EPAT for Plantar Fasciitis at Advanced Ortho and Spine
So, if you have unresolved heel pain due to plantar fasciitis, EPAT may be right for you. At Advanced Ortho and Spine, we are proud to provide EPAT to patients as a non-invasive, effective treatment for plantar fasciitis. In fact, our surgeons are regional leaders in orthopaedic surgery, dedicated to advancing orthopaedic excellence and providing the highest quality patient care.
Learn more about plantar fasciitis and EPAT in the following video.

With two locations near Nashville in Mt. Juliet and Hermitage, Advanced Ortho and Spine provides patients with high-quality, personalized care while advancing orthopaedic excellence. Contact us today to learn more or to schedule your appointment.
Disclaimer: This blog provides general information and discussions about health and related subjects. The information and other content provided in this blog, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment.If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your healthcare provider or seek other professional medical treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately.
The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice, or other institution.